Prior to the Covid-19 pandemic, one of the leading illnesses was consumption, also known as the lung disease tuberculosis (TB). The mycobacteria infection caused about 1.5 million deaths in 2018. An article in USA Today four months ago examines the history of TB consumption stating, “the disease was eradicated through elimination of poverty, improvement of nutrition and through improvement in living conditions." TB remains prevalent mostly in the developing world. Ironically, another type of consumption is afflicting the entire world by the actions of the most developed nations.
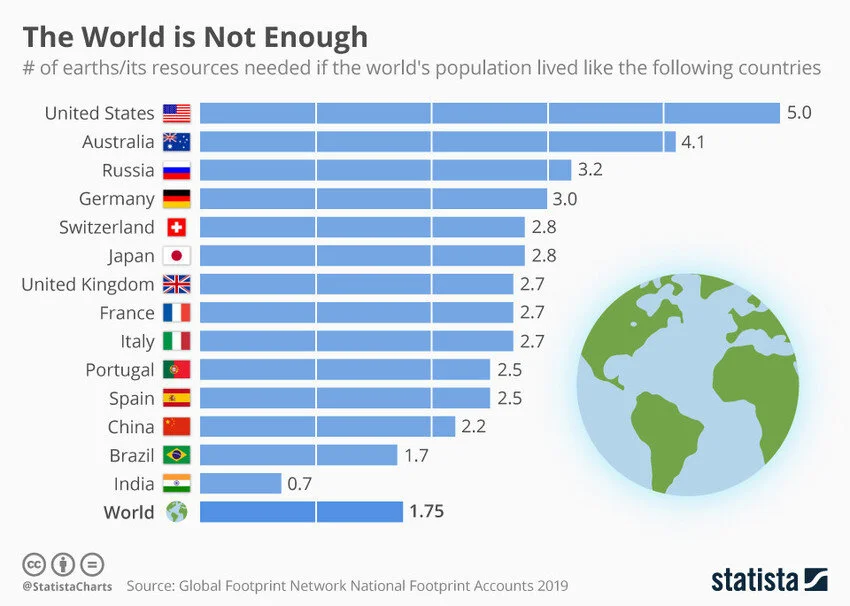
Consumption of natural resources in a consumer economy includes use of energy, food, and water. As the chart shows, people living in the United States led the world in consuming natural resources. If everyone in the world consumed resources at the rate of people in the U.S., it would take 5 Earth’s to support all the people. Obviously this is not sustainable! The World Economic Forum stated in 2019, “the extraction and processing of natural resources alone cause 90% of global biodiversity loss and water stress, and more than half of global climate change impacts.”
The U.S. has only about 4% of the world’s population yet consumes about 20% of the world’s resources. Coal-fired power plants will continue to be phased out in favor of cheaper natural gas, solar photovoltaics, wind, hydroelectric and new designs including small-modular nuclear power generation. A green energy revolution is just beginning but sustainable consumption must be considered for all industries. Powering electric car batteries with lithium oxide places demands on this metal and other rare earth elements, which are also needed for computers and wind generators. Leading producers of these raw materials are in Australia, Chile, and China. However, the U.S. will quickly be a leading importer and consumer of green energy materials and therefore continue to be dependent on imports of natural resources.
As the Covid-19 pandemic becomes even more contagious (as well as TB and other diseases), we need to carefully reassess holistic connections among health care, dependency on natural resources, and consumerism to develop global actions that preserves and protects the planet and essential biodiversity.
Some of the personal and societal solutions are quite obvious: wearing a mask, washing hands, taking vaccines, 3R’s (reduce, reuse, recycle), walking, ride a bicycle, live near your work or telecommute, carry reusable water bottles and shopping bags, and buy products that promote sustainable living.